C语言程序设计基础
函数
计算机学院 杨已彪
yangyibiao@nju.edu.cn
Review
Functions
Function Definition
Function Declaration
Arrays as Parameters
Pass by Value
Overview
(Basic) Data Types
Two Major Reasons
Architectures May Vary
Finite vs. Infinite
Object

Object Types Function Types
Data Types
The type of a variable determines
-
the set of values it may take on and
-
what operations can be performed on them.
int char bool (_Bool) double
[ ]
Integral Types (size.c)
-
(unsigned) short (int)
-
unsigned int
-
unsigned long (int)
-
unsigned long long (int)

Integral Types
-
(unsigned) short (int)
-
unsigned int
-
unsigned long (int)
-
unsigned long long (int)

Integral Types (int-limits.c)
-
(unsigned) short (int)
-
unsigned int
-
unsigned long (int)
-
unsigned long long (int)
Integral Types (exact-width.c)
int8_t int16_t int32_t int64_t

stdint.h
Signed and Unsigned (unsigned.c)
Be careful when MIXING signed and unsigned types.
typedef
typedef unsigned __int64 size_t
#define _ int64 long long {#markfont-color–bluedefinefont-font-color–red-_int64font-long-longmark }
typedef long long time_t
char (char.c)
Use char only for representing characters.
Do NOT assume signed char or unsigned char.
Overflow
(unsigned-wrap.c for-unsigned.c unsigned-wrap-fix.c)
无符号整数运算中没有溢出, 取而代之的是回绕 (wrap)现象
Overflow
(signed-overflow-fix.c)
有符号整数运算中发生溢出, 程序的行为是未定义的
Implicit Conversion
(implicit-conversion.c)
-
算术表达式、逻辑表达式 (先做整值提升 )
-
定义初始化、赋值 (类型转换)
-
函数调用时 (类型转换)
-
函数返回时 (类型转换)
Be careful about narrowing conversions!!!
Implicit Conversion
Integer promotions (integer-promotion.c)
Integer conversion rank (Section 7.4.3)
Usual arithmetic conversions (Section 7.4.1)
Explicit Conversion
(explicit-conversion.c)
(type) expression
Floating-point Numbers
(float-limits.c)
-
float (F)
-
double
-
long double (L)

“Floating-point Arithmetic is Hard.”
(Section 23.1 float.h)
“Many applications don’t need floating-point arithmetic at all.”

Use math.h (Section 23.3) whenever possible.

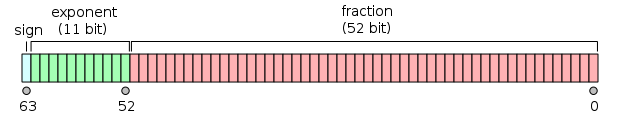
IEEE 754
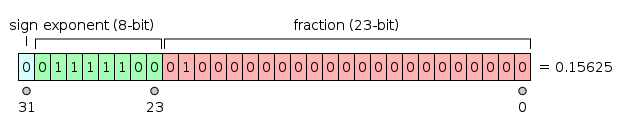
24(≈6)53(≈16)
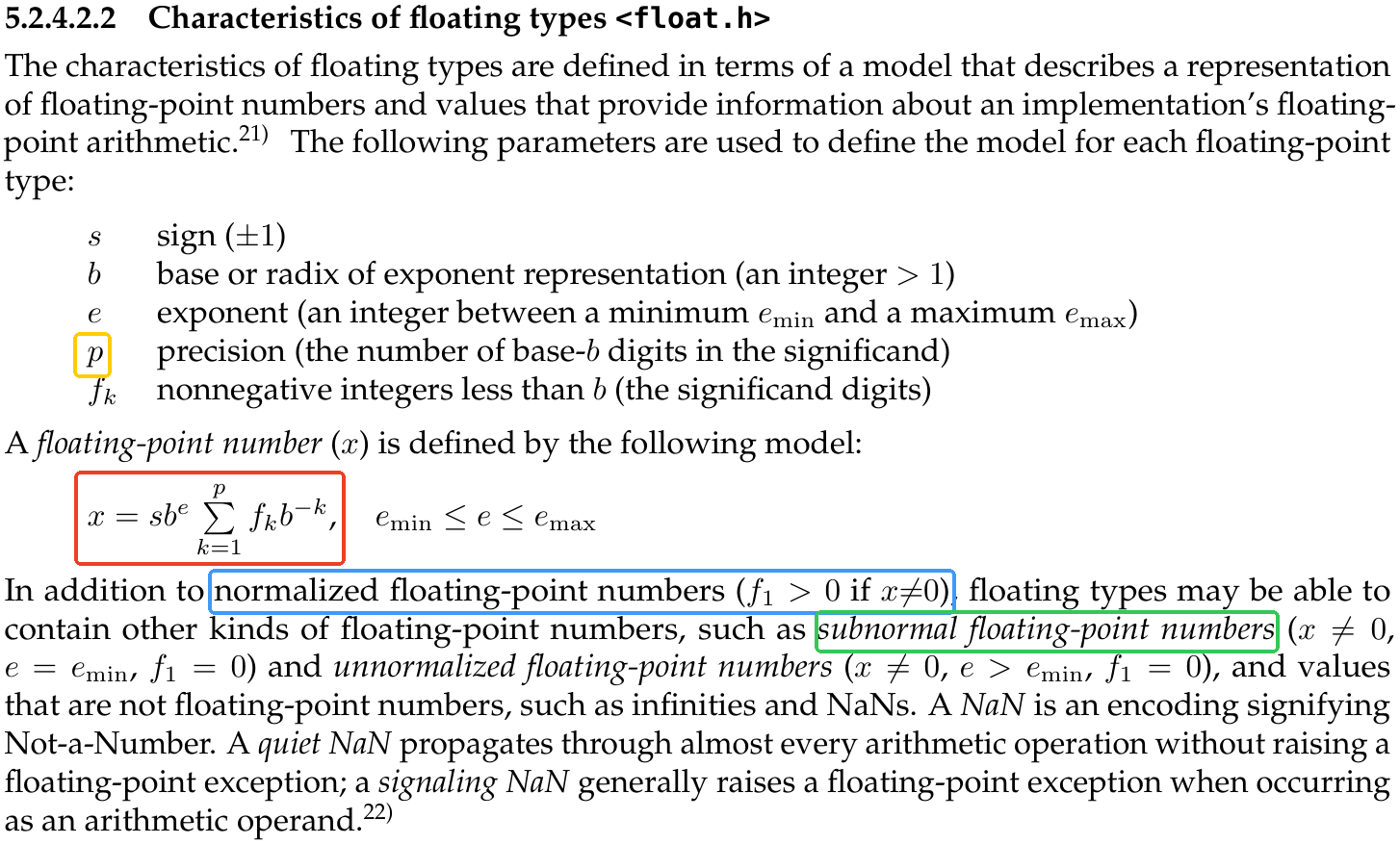
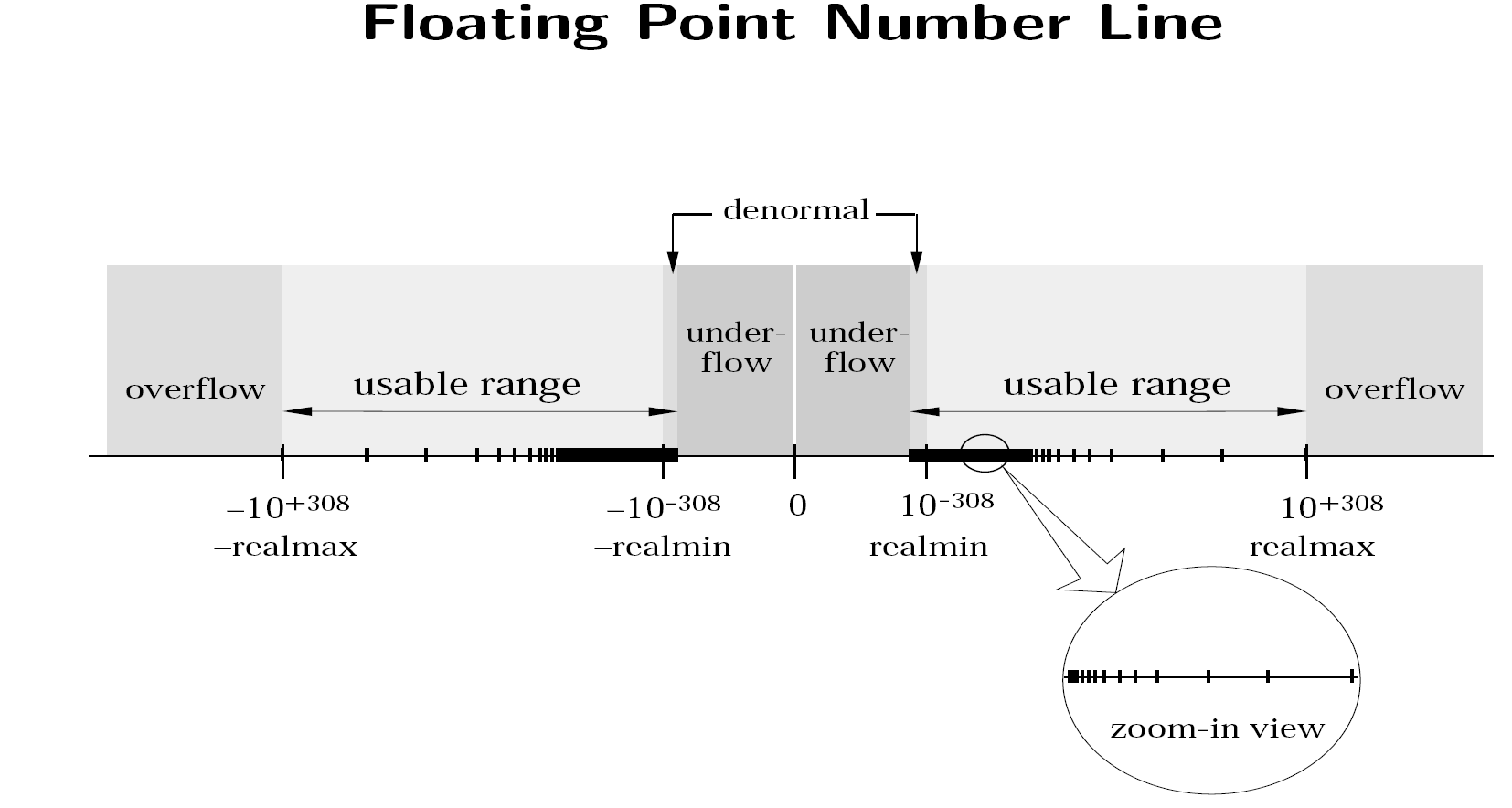
What is a subnormal floating point number? @ stackoverflow
implicit-conversion.c
sum-product.c loop.c compare.c



